In this example we show how to connect a TSL2561 is a light-to-digital converter to a MSP-EXP432P401R LaunchPad, the example will use the Energia IDE.
I used a TSL2561 module in this example, which you can see below
The TSL2561 is a light-to-digital converter that transforms light intensity to a digital signal output capable of an I²C interface. Each device combines one broadband photodiode (visible plus infrared) and one infrared-responding photodiode on a single CMOS integrated circuit capable of providing a near-photopic response over an effective 20-bit dynamic range (16-bit resolution).
Two integrating ADCs convert the photodiode currents to a digital output that represents the irradiance measured on each channel. This digital output can be input to a microprocessor where illuminance (ambient light level) in lux is derived using an empirical formula to approximate the human eye response. The TSL2561 device supports a traditional level style interrupt that remains asserted until the firmware clears it.
More info – http://ams.com/eng/Products/Light-Sensors/Ambient-Light-Sensors/TSL2561
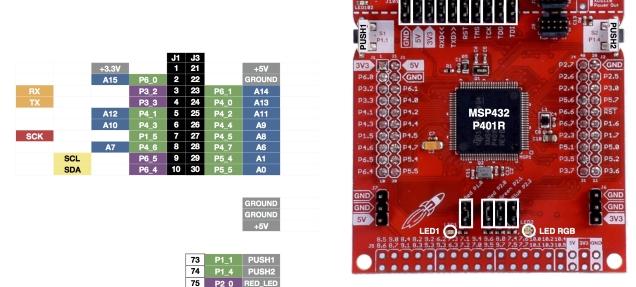
Connection
Here is a picture of the launchpad so you can see what pins we are referring to below in the table
| Module Connection | MSP432 Connection |
| SDA | J1-10 SDA |
| SCL | J1-9 SCL |
| Gnd | J3-22 Gnd |
| Vcc | J1-1 3.3v |
Code
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include<Wire.h>
// TSL2561 I2C address is 0x39(57)
#define Addr 0x39
void setup()
{
// Initialise I2C communication as MASTER
Wire.begin();
// Initialise serial communication, set baud rate = 9600
Serial.begin(9600);
// Starts I2C communication
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select control register
Wire.write(0x00 | 0x80);
// Power ON mode
Wire.write(0x03);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
// Starts I2C communication
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select timing register
Wire.write(0x01 | 0x80);
// Nominal integration time = 402ms
Wire.write(0x02);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(300);
}
void loop()
{
unsigned int data[4];
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
// Starts I2C communication
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select data register
Wire.write((140 + i));
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
// Request 1 byte of data
Wire.requestFrom(Addr, 1);
// Read 1 bytes of data
if(Wire.available() == 1)
{
data[i] = Wire.read();
}
delay(200);
}
// Convert the data
double ch0 = ((data[1] & 0xFF) * 256) + (data[0] & 0xFF);
double ch1 = ((data[3] & 0xFF) * 256) + (data[2] & 0xFF);
// Output data to serial monitor
Serial.print("Full Spectrum(IR + Visible) :");
Serial.println(ch0);
Serial.print("Infrared Value :");
Serial.println(ch1);
Serial.print("Visible Value :");
Serial.println(ch0-ch1);
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open the serial monitor and you should see something like this
Full Spectrum(IR + Visible) :184.00
Infrared Value :25.00
Visible Value :159.00
Full Spectrum(IR + Visible) :176.00
Infrared Value :12.00
Visible Value :164.00
Full Spectrum(IR + Visible) :8.00
Infrared Value :2.00
Visible Value :6.00
Full Spectrum(IR + Visible) :8.00
Infrared Value :11.00
Visible Value :-3.00
Full Spectrum(IR + Visible) :141.00
Infrared Value :22.00
Visible Value :119.00
Links
1pcs GY-2561 TSL2561 Luminosity Sensor Breakout infrared Light Sensor module integrating sensor AL