The ADXL345 is a small, thin, low power, 3-axis accelerometer with high resolution (13-bit) measurement at up to ±16g. Digital output data is formatted as 16-bit twos complement and is accessible through either a SPI (3- or 4-wire) or I2C digital interface.
The ADXL345 is well suited for mobile device applications. It measures the static acceleration of gravity in tilt-sensing applications, as well as dynamic acceleration resulting from motion or shock. Its high resolution (4 mg/LSB) enables measurement of inclination changes less than 1.0°.
Several special sensing functions are provided. Activity and inactivity sensing detect the presence or lack of motion and if the acceleration on any axis exceeds a user-set level. Tap sensing detects single and double taps. Free-fall sensing detects if the device is falling. These functions can be mapped to one of two interrupt output pins. An integrated, patent pending 32-level first in, first out (FIFO) buffer can be used to store data to minimize host processor intervention.
Features
- Ultralow power: as low as 23 μA in measurement mode and 0.1 μA in standby mode at VS = 2.5 V (typical)
- Power consumption scales automatically with bandwidth
- User-selectable resolution
- Fixed 10-bit resolution
- Full resolution, where resolution increases with g range, up to 13-bit resolution at ±16 g (maintaining 4 mg/LSB scale factor in all g ranges)
Parts List
| Label | Part Type | |
|---|---|---|
| MBED1 | mbed LPC 1768 | |
| Part1 | Adafruit ADXL345 |
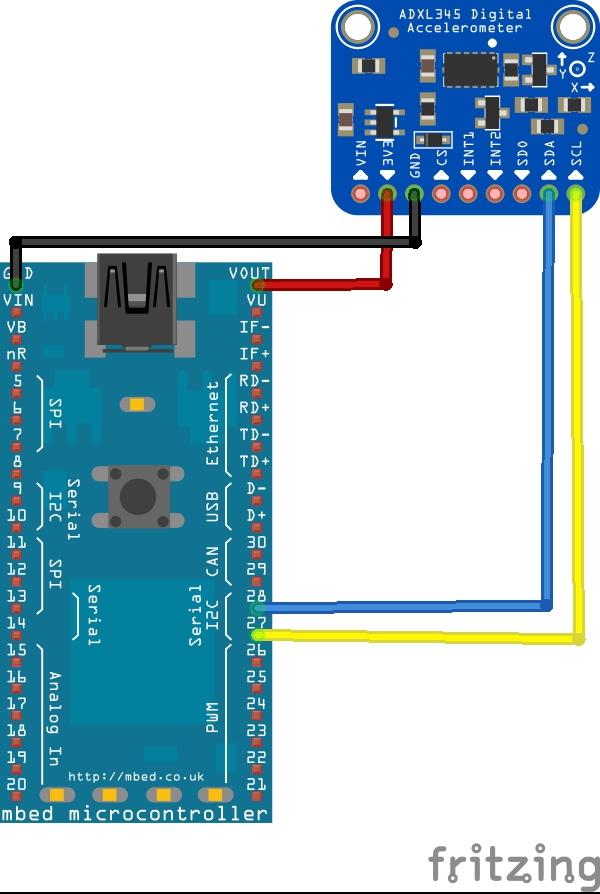
Layout
Code
You will need to import the library from https://os.mbed.com/components/ADXL345-Accelerometer/ and I used the I2C example as well, which you can see below
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include "ADXL345_I2C.h"
ADXL345_I2C accelerometer(p28, p27);
Serial pc(USBTX, USBRX);
int main()
{
pc.baud(115200);
int readings[3] = {0, 0, 0};
pc.printf("Starting ADXL345 test...\n");
wait(.001);
pc.printf("Device ID is: 0x%02x\n", accelerometer.getDeviceID());
wait(.001);
// These are here to test whether any of the initialization fails. It will print the failure
if (accelerometer.setPowerControl(0x00))
{
pc.printf("didn't intitialize power control\n");
return 0;
}
//Full resolution, +/-16g, 4mg/LSB.
wait(.001);
if(accelerometer.setDataFormatControl(0x0B))
{
pc.printf("didn't set data format\n");
return 0;
}
wait(.001);
//3.2kHz data rate.
if(accelerometer.setDataRate(ADXL345_3200HZ))
{
pc.printf("didn't set data rate\n");
return 0;
}
wait(.001);
//Measurement mode.
if(accelerometer.setPowerControl(MeasurementMode))
{
pc.printf("didn't set the power control to measurement\n");
return 0;
}
while (1)
{
wait(0.5);
accelerometer.getOutput(readings);
pc.printf("%i, %i, %i\r\n", (int16_t)readings[0], (int16_t)readings[1], (int16_t)readings[2]);
}
}
[/codesyntax]
Testing
Using a terminal program like Teraterm you should see something like this
-320, 226, 164
-254, -8, 94
-12, -168, -70
-172, -210, 60
-76, -38, -162
-198, 322, 130
-42, -254, -8
-126, 228, 0
-140, 70, -92
-342, 66, 46
-122, 156, 158
-78, 148, 204
Links
GY-291 ADXL345 3-Axis Digital Gravity Sensor Acceleration Module IIC/SPI transmission