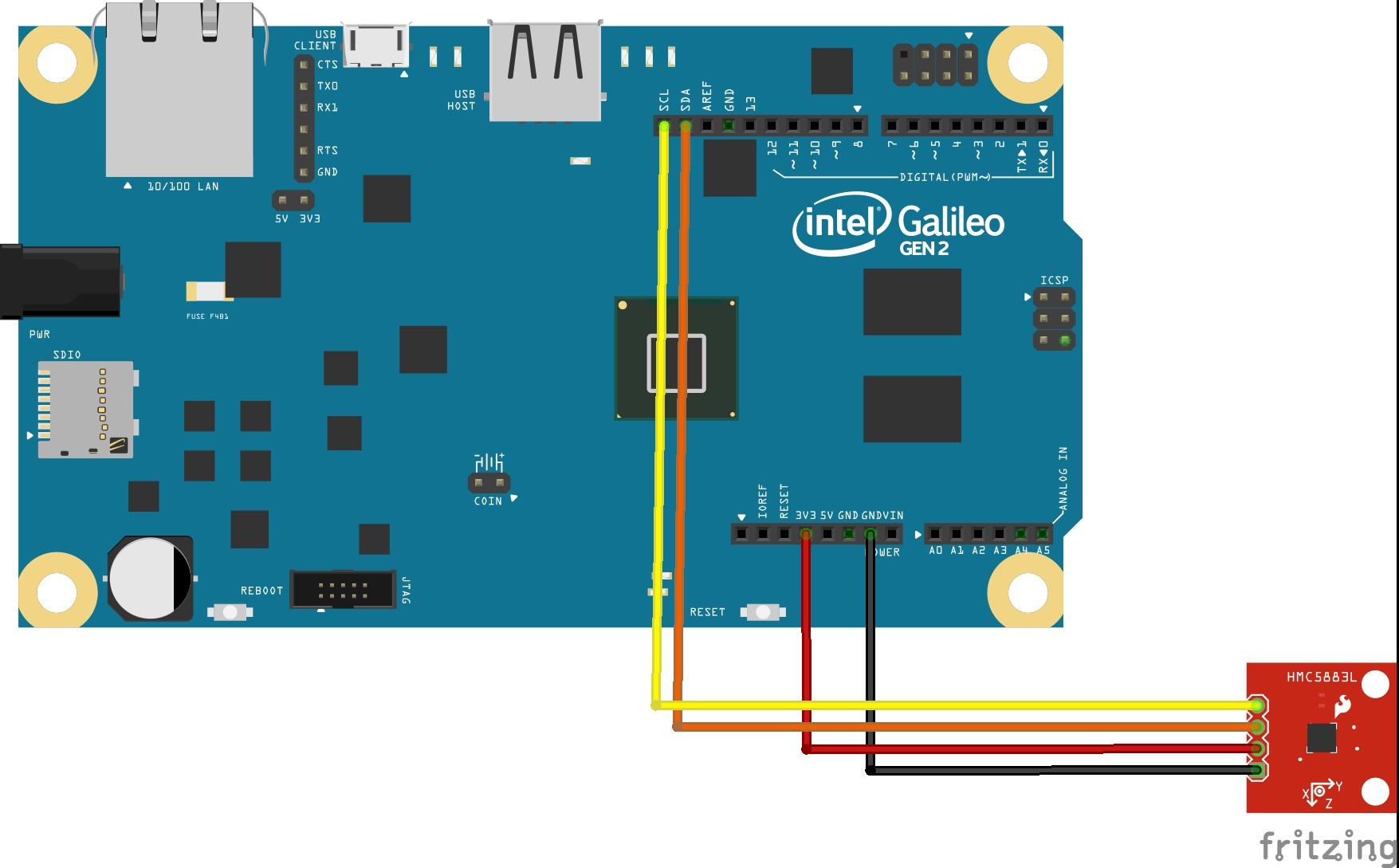
In this example we connect a HMC5883L sensor to an Intel Galileo
The Honeywell HMC5883L is a surface-mount, multi-chip module designed for low-field magnetic sensing with a digital interface for applications such as lowcost compassing and magnetometry. The HMC5883L includes our state-of-the art, high-resolution HMC118X series magneto-resistive sensors plus an ASIC containing amplification, automatic degaussing strap drivers, offset cancellation, and a 12-bit ADC that enables 1° to 2° compass heading accuracy.
The I2C serial bus allows for easy interface. The HMC5883L is a 3.0×3.0x0.9mm surface mount 16-pin leadless chip carrier (LCC). Applications for the HMC5883L include Mobile Phones, Netbooks, Consumer Electronics, Auto Navigation Systems, and Personal Navigation Devices.
The HMC5883L utilizes Honeywell’s Anisotropic Magnetoresistive (AMR) technology that provides advantages over other magnetic sensor technologies. These anisotropic, directional sensors feature precision in-axis sensitivity and linearity. These sensors’ solid-state construction with very low cross-axis sensitivity is designed to measure both the direction and the magnitude of Earth’s magnetic fields, from milli-gauss to 8 gauss. Honeywell’s Magnetic Sensors are among the most sensitive and reliable low-field sensors in the industry.
Parts List
| Label | Part Type |
|---|---|
| Part1 | Intel Galileo Gen2 |
| Part3 | Triple Axis Magnetometer – HMC5883 Breakout |
Layout
Code
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include<Wire.h>
// HMC5883 I2C address is 0x1E(30)
#define Addr 0x1E
void setup()
{
// Initialise I2C communication as MASTER
Wire.begin();
// Initialise Serial Communication, set baud rate = 9600
Serial.begin(9600);
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select configure register A
Wire.write(0x00);
// Set normal measurement configuration, data output rate = 0.75Hz
Wire.write(0x60);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select Mode register
Wire.write(0x02);
// Set continuous measurement
Wire.write(0x00);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(300);
}
void loop()
{
unsigned int data[6];
// Start I2C Transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(Addr);
// Select data register
Wire.write(0x03);
// Stop I2C Transmission
Wire.endTransmission();
// Request 6 bytes of data
Wire.requestFrom(Addr, 6);
// Read 6 bytes of data
// xMag msb, xMag lsb, zMag msb, zMag lsb, yMag msb, yMag lsb
if(Wire.available() == 6)
{
data[0] = Wire.read();
data[1] = Wire.read();
data[2] = Wire.read();
data[3] = Wire.read();
data[4] = Wire.read();
data[5] = Wire.read();
}
delay(300);
// Convert the data
int xMag = ((data[0] * 256) + data[1]);
int zMag = ((data[2] * 256) + data[3]);
int yMag = ((data[4] * 256) + data[5]);
// Output data to serial monitor
Serial.print("Magnetic Field in X-Axis : ");
Serial.println(xMag);
Serial.print("Magnetic Field in Y-Axis : ");
Serial.println(yMag);
Serial.print("Magnetic Field in Z-Axis : ");
Serial.println(zMag);
delay(300);
}
[/codesyntax]
Testing
Open up a serial monitor and you should see something like this
Magnetic Field in X-Axis : 50
Magnetic Field in Y-Axis : 64804
Magnetic Field in Z-Axis : 42
Magnetic Field in X-Axis : 50
Magnetic Field in Y-Axis : 64804
Magnetic Field in Z-Axis : 42
Magnetic Field in X-Axis : 65182
Magnetic Field in Y-Axis : 65491
Magnetic Field in Z-Axis : 330
Magnetic Field in X-Axis : 65182
Magnetic Field in Y-Axis : 65491
Magnetic Field in Z-Axis : 330
Magnetic Field in X-Axis : 65182
Magnetic Field in Y-Axis : 65491
Magnetic Field in Z-Axis : 330
Magnetic Field in X-Axis : 65202
Magnetic Field in Y-Axis : 65317
Magnetic Field in Z-Axis : 371
Links
HMC5883 GY-271 3V-5V Triple Axis Compass Magnetometer Sensor Module For Arduino