This 16-bit I/O expander for the two-line bidirectional bus (I2C) is designed for 2.5-V to 5.5-V VCCoperation.
The PCF8575 device provides general-purpose remote I/O expansion for most microcontroller families by way of the I2C interface [serial clock (SCL), serial data (SDA)].
The device features a 16-bit quasi-bidirectional input/output (I/O) port (P07–P00, P17–P10), including latched outputs with high-current drive capability for directly driving LEDs. Each quasi-bidirectional I/O can be used as an input or output without the use of a data-direction control signal. At power on, the I/Os are high. In this mode, only a current source to VCC is active.
Features
- I2C to Parallel-Port Expander
- Open-Drain Interrupt Output
- Low Standby-Current Consumption of 10 µA Max
- Compatible With Most Microcontrollers
- 400-kHz Fast I2C Bus
- Address by Three Hardware Address Pins for Use
of up to Eight Devices - Latched Outputs With High-Current Drive
Capability for Directly Driving LEDs - Current Source to VCC for Actively Driving a High
at the Output
Here is a handy little module that saves the hassle of buying smt chips and making your own breakouts
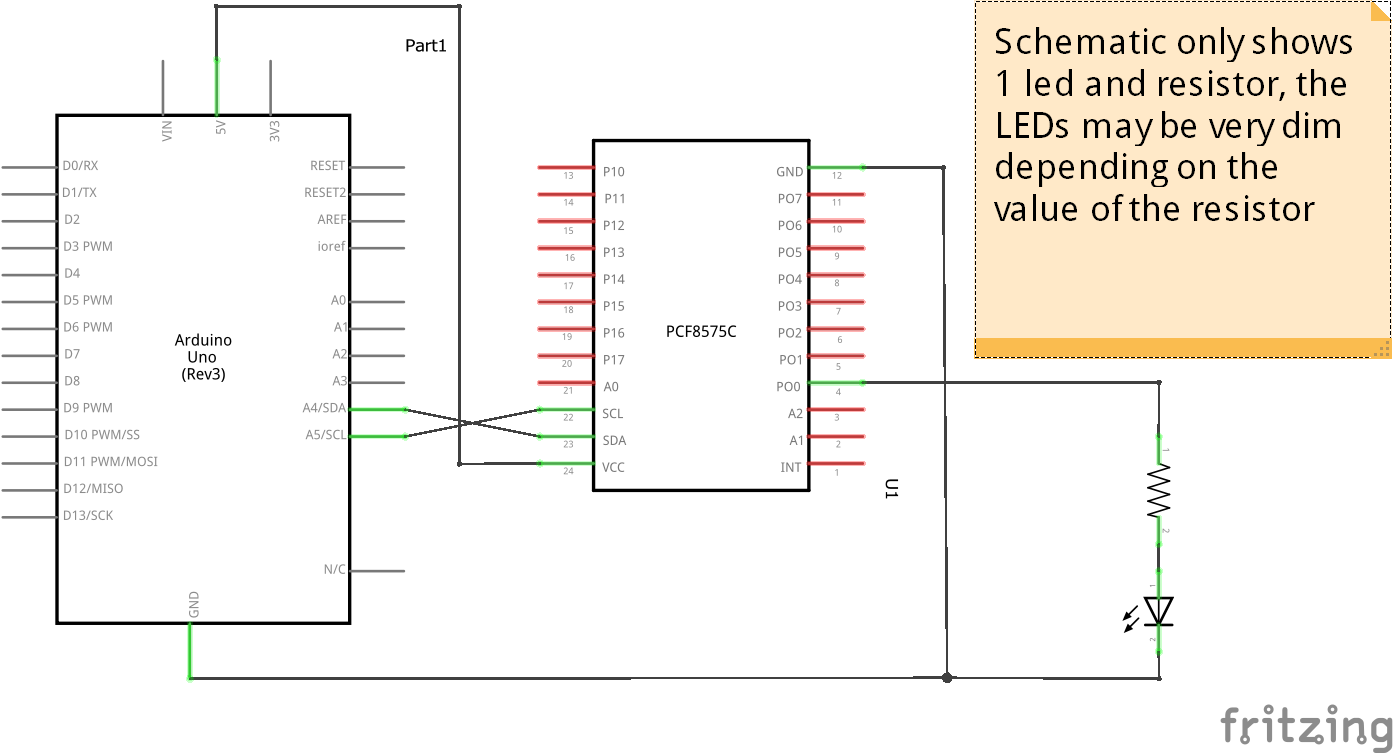
Schematic
This is a basic schematic showing only 1 test LED, you would create a test board with 8 or even 16 if you wanted to test both ports on the PCF8575
Code
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Wire.h>
byte address = 0x20; // address of PCF8575
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus as master
}
void loop()
{
unsigned char x;
unsigned char y;
for (x=0, y=255; (x+y)==255; x++, y--)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(address); // send the address and the write cmnd
Wire.write(x); // pack the first byte
Wire.write(y); // pack the second byte
Wire.endTransmission(); // send the data
delay(150);
}
}
[/codesyntax]
Link
PCF8575 IIC I2C I/O Extension Shield Module 16 bit SMBus I/O ports