When we create a function, it must be given a name. The naming convention for functions is the same as for variables:
•The function name can be made up of alphanumeric characters (A to Z; a to z; 0 to 9) and the underscore (_).
•The function name may not start with a number
•A function name must not be used that is the same as a language keyword or existing function.
A function must have a return type. If teh example function does not return anything, it will have a return type of void.
The function body is made up of a variety of statements placed between braces {}.
1) each function must have a unique name,
2) the function name is followed by parentheses ()
3) functions have a return type, e.g. void,
4) the body of a function is enclosed in opening and closing braces {}.
To call the function, you use the function name followed by opening and closing parentheses and then put a semi colon after it.
There are advantages of using functions is that they avoid having to write the same code over and over again. Every time you call a function, we are just reusing code that has been written once.
If you were to write code that say performed the same task 5 times then if you wished to update this for some reason you would have to modify the code in 5 places but if you were to use a function and call it 5 times then all you have to do is modify the function. Functions can be used to break a sketch up into pieces which make it easier to understand.
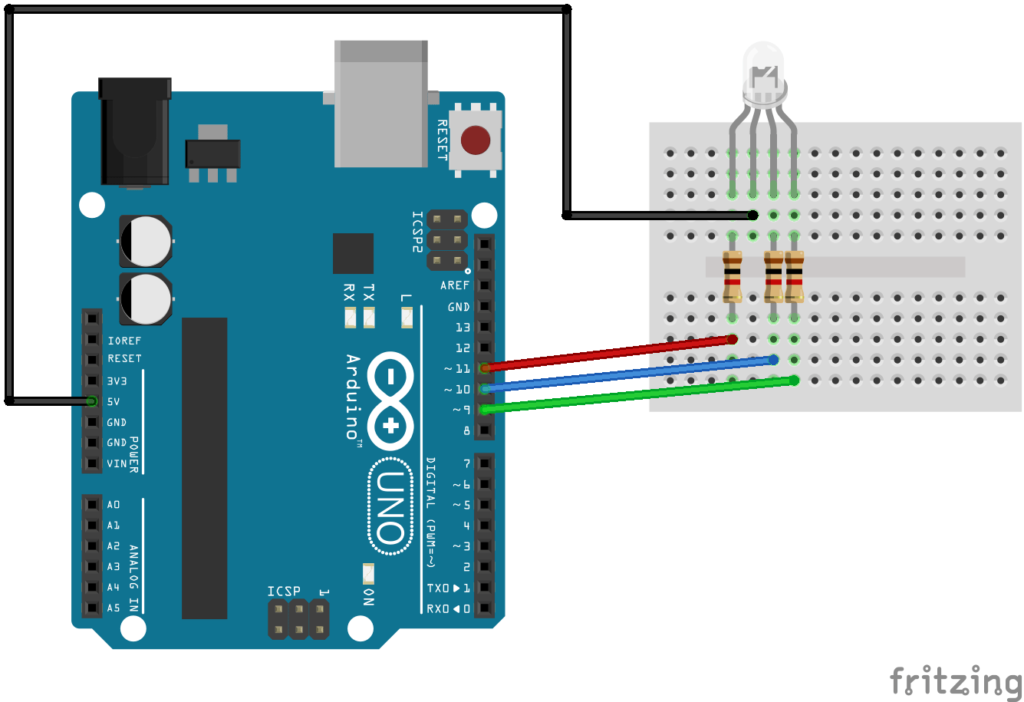
We are using the following circuit in the example later
We will take some of the code we created in previous tutorials and adapt this to use functions instead
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
int redled = 11;
int blueled = 10;
int greenled = 9;
void setup()
{
pinMode(redled, OUTPUT); //set the LED pin as an output
pinMode(blueled, OUTPUT); //set the LED pin as an output
pinMode(greenled, OUTPUT); //set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop()
{
int i = 1;
AllOff();
delay(1000);
while(i<=3)
{
switch (i)
{
case 1:
RedOn();
delay(1000);
break;
case 2:
BlueOn();
delay(1000);
break;
case 3:
GreenOn();
delay(1000);
break;
default:
break;
}
i++;
}
}
void AllOff()
{
digitalWrite(redled, HIGH); // red led off
digitalWrite(blueled, HIGH); //blue led off
digitalWrite(greenled, HIGH); //green led off
}
void RedOn()
{
digitalWrite(redled, LOW); // red led on
digitalWrite(blueled, HIGH); //blue led off
digitalWrite(greenled, HIGH); //green led off
}
void BlueOn()
{
digitalWrite(redled, HIGH); // red led off
digitalWrite(blueled, LOW); //blue led on
digitalWrite(greenled, HIGH); //green led off
}
void GreenOn()
{
digitalWrite(redled, HIGH); // red led off
digitalWrite(blueled, HIGH); //blue led off
digitalWrite(greenled, LOW); //green led on
}
[/codesyntax]